“Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Mural Thrombus: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies for Optimal Health”
Mural thrombus might not be a familiar term, but it’s vital to shed light on it. This condition can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Therefore, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial.
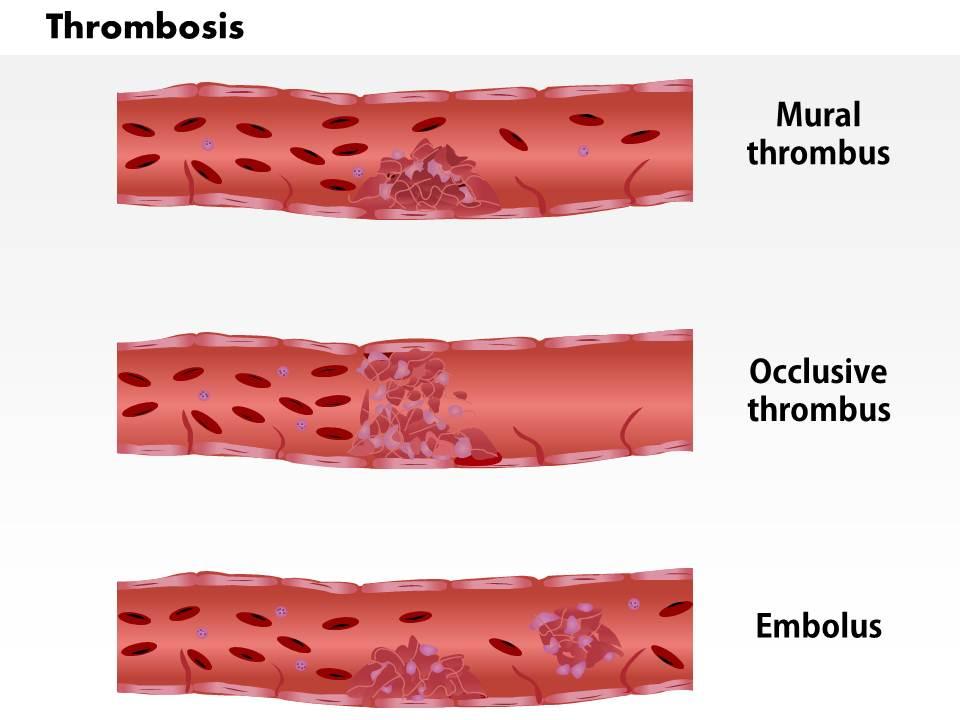
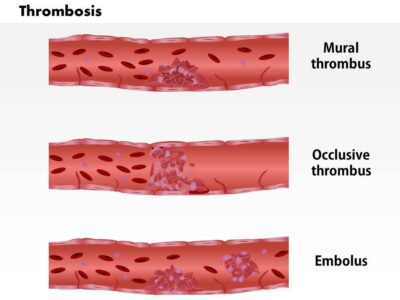
What Is Mural Thrombus? Mural thrombus involves the formation of blood clots within the walls of blood vessels, typically arteries or veins. Unlike typical blood clots within the lumen of blood vessels, mural thrombi adhere to the vessel walls, presenting unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Mural Thrombus:
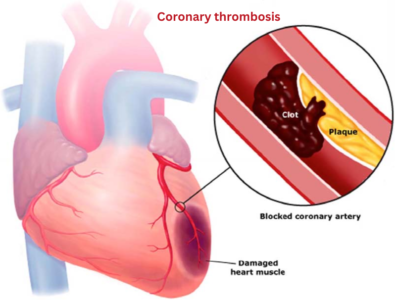
- Atherosclerosis: A common cause of mural thrombus is atherosclerosis. It’s characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits and plaque on artery walls, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Aneurysms: Aneurysms, bulges or weak areas in blood vessel walls, can cause turbulence in blood flow, leading to mural thrombi formation.
- Endocarditis: This heart lining infection can cause clots along the heart’s chambers, which may dislodge and cause mural thrombi in other parts of the body.
Symptoms of Mural Thrombus: Mural thrombus often remains asymptomatic until it triggers other health issues. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain: You may experience localized pain depending on the thrombus’s location.
- Numbness and Weakness: If blood flow to an organ or extremity is affected, it can lead to numbness and weakness.
- Ischemia: Mural thrombi can cause tissue ischemia, resulting in tissue damage and organ dysfunction.
- Embolic Complications: Mural thrombi can dislodge, causing embolic complications such as strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolism.
Diagnosis: Diagnosing mural thrombus (MT)can be challenging due to its often inconspicuous symptoms. Healthcare professionals use various diagnostic tools to detect and confirm its presence:
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, Doppler imaging, and CT scans provide detailed images of blood vessels, aiding in identifying the thrombus’s location and size.
- Blood Tests: These can detect abnormal clotting factors, indicating the presence of a thrombus.
- Echocardiography: This test assesses heart function and identifies thrombi within the heart chambers.
Treatment Options: (MT)treatment depends on its location, size, and potential complications. Common treatments include:
- Anticoagulants: Medications like heparin and warfarin are prescribed to prevent thrombus growth and reduce embolic risk.
- Thrombolytic Therapy: In severe cases, thrombolytic therapy may dissolve the clot.
- Surgical Removal: Surgical removal is necessary in cases with large or severe thrombus risks.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: Treating conditions like atherosclerosis, aneurysms, or endocarditis is vital to prevent thrombus recurrence.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes: Preventing mural thrombus involves addressing underlying causes. Lifestyle changes that can reduce risk include:
- Healthy Diet: Reducing saturated fats and cholesterol in your diet helps prevent atherosclerosis.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes healthy blood flow and prevents clots.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is a major atherosclerosis risk factor, so quitting reduces the risk.
- Controlling Blood Pressure and Diabetes: Managing these conditions helps prevent (MT)development.
Mural thrombus is a potentially severe condition requiring early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for maintaining vascular health. If you suspect (MT)or are at risk due to an underlying condition, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance. Early intervention and knowledge can significantly impact your well-being.